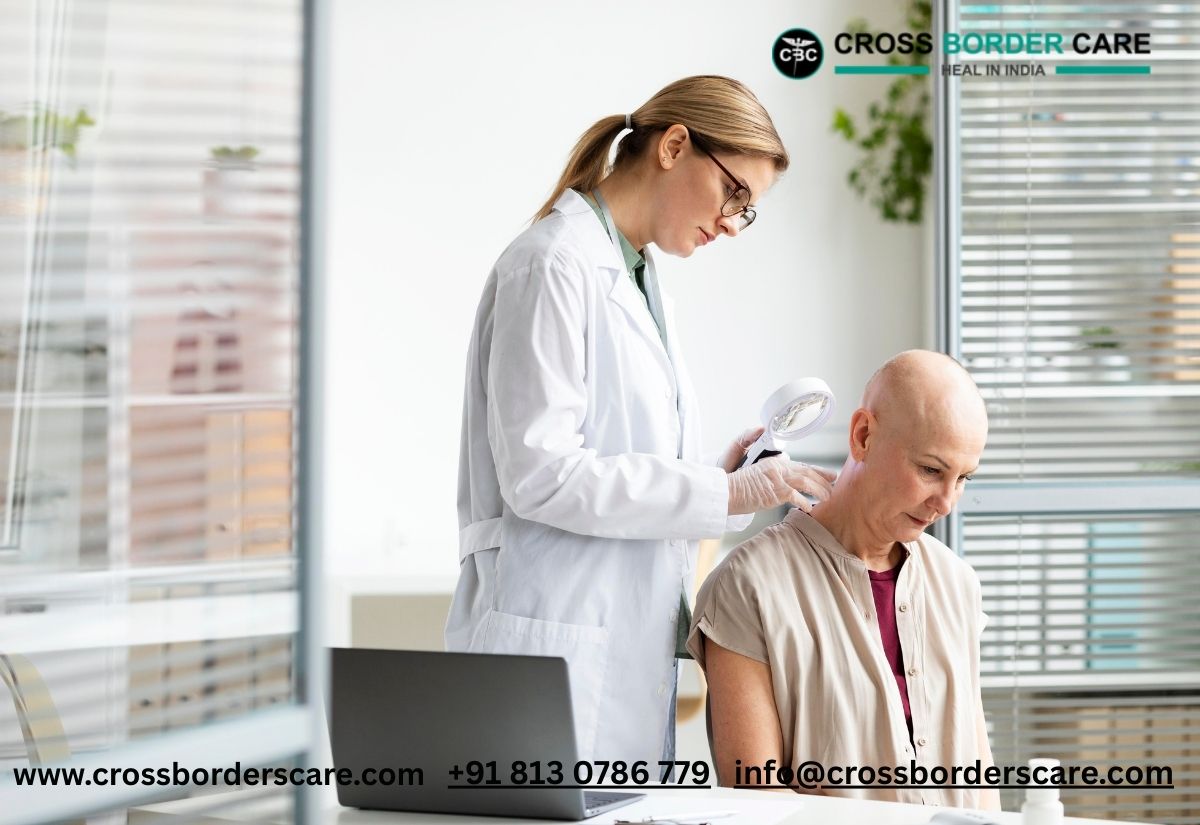
A prostatectomy can surgically remove the prostate gland. This can be done for various reasons, such as managing specific benign prostatic diseases or treating prostate cancer. There are many types of prostatectomies, including transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), which removes a portion of the prostate through the urethra, and radical Prostatectomy, which removes the entire prostate gland. The exact medical issue and the severity of the case determine the treatment to be used. Prostatectomy surgery in India is a safe and effective procedure for patients who suffer from prostate-related conditions. A healthcare expert should be consulted for detailed information and counseling.
Purpose
A prostatectomy is primarily performed to treat diseases associated with the prostate gland. The patient’s condition and unique circumstances help to determine the type of Prostatectomy and surgical strategy that will be performed. Depending on the underlying ailment, this surgical technique may have several objectives:
- Treating prostate cancer: Treatment for prostate cancer is one of the most frequent uses of a prostatectomy. If the cancer is limited and hasn’t migrated to other parts of the body, the aim is to remove the malignant prostate tissue in this scenario.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): A prostatectomy may be performed to remove extra prostate tissue that is obstructing the urethra and causing urinary issues in cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia. In benign prostatic hyperplasia, an enlarged prostate can cause urine symptoms. This primarily aims to alleviate urinary problems.
- Prostatitis: In extremely rare instances of severe and persistent prostatitis (prostate inflammation), a prostatectomy may be an option as a last resort to relieve symptoms that haven’t improved with other therapies.
Types
The patient’s medical condition, the size of the prostate, the existence of cancer, and the surgeon’s experience all play an important role in choosing the type of Prostatectomy that is performed. The patient must consult a healthcare professional before undergoing the procedure. Here are the main types of Prostatectomy:
- Radical Prostatectomy: The most popular form of Prostatectomy for the treatment of prostate cancer is radical Prostatectomy. The entire prostate gland, as well as any adjacent lymph nodes, must be removed. Different methods can be used to perform a radical prostatectomy:
- Open surgery: A significant abdominal incision is made to access the prostate.
- Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A minimally invasive procedure in which the surgeon is guided via a camera through small incisions.
- Robotic-assisted laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A laparoscopic surgery in which the surgeon is helped by a robotic technology to carry out the process more precisely.
- Robotic-assisted laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A laparoscopic surgery in which the surgeon is helped by a robotic technology to carry out the process more precisely.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is treated with the transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). The extra prostate tissue blocking the urethra is removed rather than the complete prostate. The urethra usually does this procedure through specialized devices.
- Transurethral prostate incision (TUIP): Similar to TURP, transurethral prostate incision (TUIP) is used to treat BPH. To treat urinary problems, tiny incisions are made in the prostate gland. It is typically used for BPH situations that are less severe.
- Simple Prostatectomy: This surgery is utilized when TURP or TUIP is ineffective for treating very big prostates. It entails keeping the prostate’s outer shell intact while just removing the inner portion of the prostate that is obstructing the urinary tract.
- Laser techniques: Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) and GreenLight laser therapy are two examples of laser techniques that can be used to treat BPH. These methods reduce urinary problems by vaporizing or removing extra prostate tissue with laser radiation.
Procedure
Whether it’s a radical prostatectomy for cancer or a less invasive procedure for benign disorders like BPH, the prostatectomy procedure may vary depending on the type of surgery being done. The most common method of Prostatectomy involves the following fundamental steps:
- Preparation: The patient will normally undergo several medical examinations and tests before surgery to determine their general health and fitness for the procedure. They might also need to change their medication and adhere to certain dietary requirements.
- Anesthesia: The patient receives either regional anesthesia, which numbs the lower body, including the surgical area, or general anesthesia, which puts them into a deep sleep.
- Incision: An incision will be made in the abdomen or the lower section, depending on the surgical method (open, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted). Small incisions are made to allow specialized equipment and a camera during robotic or laparoscopic treatments.
- Prostate Removal: The surgeon meticulously dissects and removes the entire prostate gland and any potentially cancerous lymph nodes or surrounding tissues. All malignant tissue must be removed, but surrounding tissues, including blood vessels and nerves necessary for sexual and urine function, must be preserved.
- Reconstruction: The surgeon may repair the urinary system after removing the prostate. To restore urine function, the bladder may need to be sutured back to the urethra.
- Closure: The incisions are stitched or stapled shut by the surgeon, and the surgical site is dressed or bandaged.
- Recovery: Patients who emerge from anesthesia are closely watched in a recovery area. The time that a patient stays in the hospital for recovery will depend on the type of surgery they underwent and their health. Everybody recovers differently following a prostatectomy, but most people need time to relax and heal.
Risks
Like any other surgical procedure, prostatectomies have possible risks. The risks may vary depending on the type of Prostatectomy performed and the patient’s health. The following are some typical dangers of Prostatectomy:
- Bleeding: Both during and after surgery, bleeding can occur. Additional surgical operations can be required in some cases to stop bleeding.
- Infection: The urinary tract and the surgical site are at risk of contracting an infection. Antibiotics are frequently effective in treating this, although other treatments can also be used.
- Blood Clots: Patients undergoing surgery risk developing blood clots, which may spread to other parts of the body or the lungs.
- Urine Incontinence: Some men who have undergone Prostatectomy may have urine incontinence, which can range from little leakage to total loss of urinary control, either temporarily or permanently.
- Erectile Dysfunction: After a prostatectomy, men may develop temporary or permanent erectile dysfunction depending on the surgical strategy and the level of nerve-sparing treatments.
- Damage to Surrounding Structures: During surgery, it’s possible to unintentionally harm nearby structures like the rectum, blood arteries, or nerves.
- Complications of anesthesia: Anesthesia has its dangers, such as unfavorable reactions, respiratory issues, or allergies.
- Recurrence: Even after a successful prostatectomy, prostate cancer patients still have the chance of a cancer relapse. This can call for additional care, such as radiation or hormone therapy.
Recovery
Recovery time after prostatectomy can vary from person to person. Here is some general advice on healing that can be useful:
- Follow Medical Advice: Comply with any prescription directions, wound care instructions, and other post-operative advice from your surgeon and medical staff.
- Activity and Rest: While taking it easy and letting your body heal is vital, doing some light exercise is also crucial. Walking is frequently advised to enhance circulation and prevent blood clots.
- Pain Control: If you’re in too much pain, take your painkillers as directed and let your medical staff know.
- Diet: Comply with any dietary recommendations made by your medical experts. Healing can be aided by drinking plenty of water and eating a healthy diet.
- Exercises for the Pelvic Floor: Kegel exercises for the pelvic floor, also known as pelvic floor exercises, can aid with bladder control. Ask the doctor to explain them in detail.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: To prevent strain on the surgical area, refrain from heavy lifting or hard activity for a few weeks or as directed by your surgeon.
- Take care of the incision: Maintain the surgical incision clean and dry. Change dressings according to instructions, and report any infection-related symptoms such as edema, discharge, or increasing redness.
For prostate-related conditions, prostatectomy surgery in India offers cutting-edge solutions. With skilled surgeons and state-of-the-art facilities, patients can get effective treatments here.
October 1, 2023