When it comes to women’s cancer care in India, two of the most commonly misunderstood types are uterine cancer and cervical cancer. Though both occur in the female reproductive system, they are not the same. These two cancers differ in their origin, symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment approaches. Understanding their distinctions is critical for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective cancer treatment in India.
As your trusted partner in healthcare, Cross Border Care, India’s best medical consultant, brings you clarity on this crucial topic so you can make informed decisions for yourself or your loved ones.
Uterine Cancer Vs Cervical Cancer
Origin
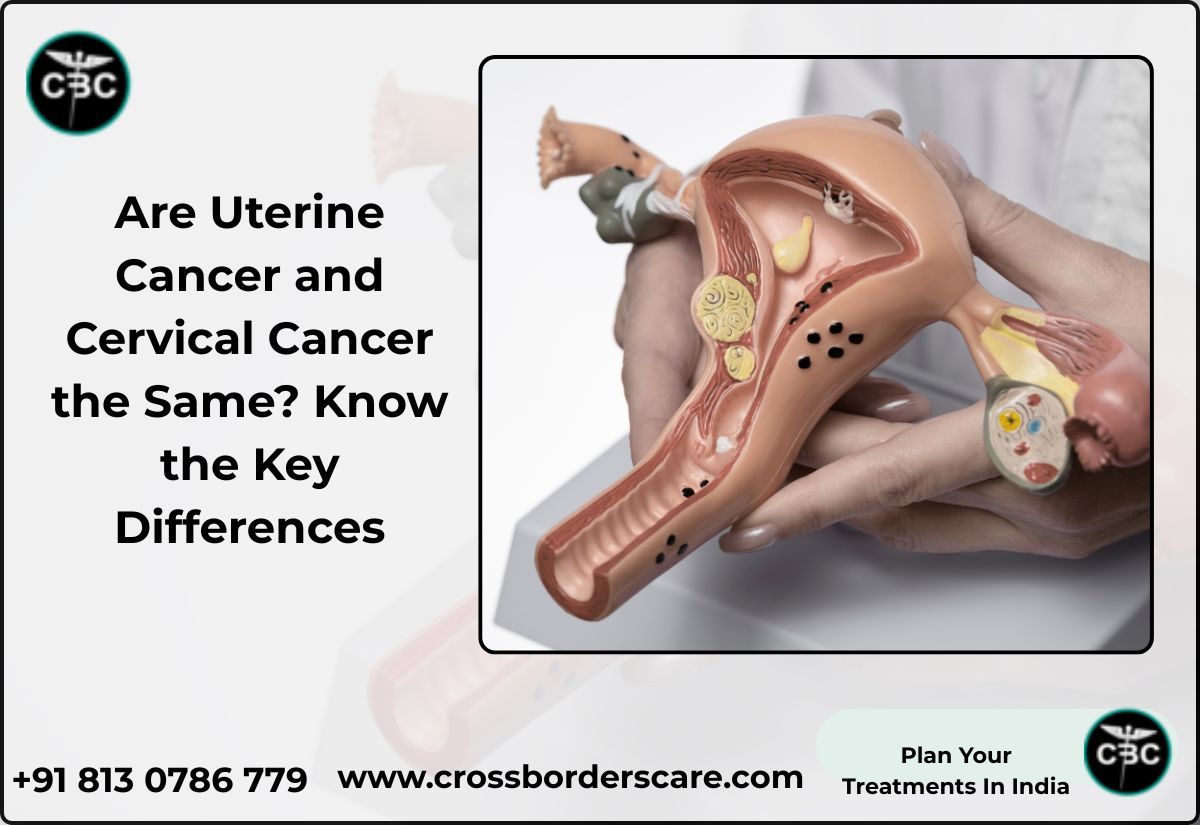
Uterine Cancer (Endometrial Cancer):
Uterine cancer originates in the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. This lining thickens monthly in preparation for pregnancy and sheds during menstruation. Abnormal cell growth in this lining leads to uterine cancer. Contact us today for uterine cancer treatment in India.
Cervical Cancer:
Cervical cancer begins in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It usually develops from persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV). The transformation zone of the cervix, where two types of cells meet, is where cervical cancer typically starts.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Though some symptoms overlap, knowing what to look for can guide early diagnosis and improve outcomes for cancer treatment in India.
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding, especially after menopause
- Bleeding between periods
- Pelvic pain
- Unexplained weight loss
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer:
- Abnormal bleeding after intercourse or menopause
- Watery or bloody vaginal discharge
- Pain during sex
- Pelvic discomfort
The best oncologists in India emphasize that being alert to these warning signs and seeking medical evaluation early can lead to a timely diagnosis and better prognosis.
Understanding Risk Factors
While both cancers share some risk factors, there are unique contributors to each:
| Cervical Cancer | Uterine Cancer |
|---|---|
| HPV infection | Obesity |
| Multiple sexual partners | Hormone replacement therapy |
| Smoking | Older age/postmenopause |
| Weakened immunity | Family history of uterine cancer |
Preventive steps like HPV vaccination, safe sexual practices, and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of both.
How Are They Diagnosed?
Cervical Cancer Diagnosis:
- Pap Smear: Detects abnormal cervical cells before they become cancerous.
- HPV Testing: Identifies high-risk strains of HPV.
- Colposcopy and Biopsy: Provides a closer look at the cervix and confirms the diagnosis.
Uterine Cancer Diagnosis:
- Endometrial Biopsy: Collects tissue from the uterine lining for testing.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Measures endometrial thickness.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Samples more tissue if needed.
Regular screenings and early check-ups at leading cancer hospitals in India can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Treatment Options in India
Uterine Cancer Treatment in India
- Surgery (Hysterectomy): Surgical removal of the uterus is the most common and effective treatment for early-stage uterine cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors in the pelvic region.
- Chemotherapy: Cancer-killing drugs are administered to treat advanced or recurrent uterine cancer.
- Hormone Therapy: Medications are used to block hormones that fuel the growth of certain uterine cancers.
Cervical Cancer Treatment in India
- Surgery (e.g., cone biopsy, trachelectomy): Surgical options remove cancerous tissue and preserve fertility in early-stage cervical cancer.
- Radiation and Chemotherapy: Often used together to treat locally advanced cervical cancer or after surgery to prevent recurrence.
- Targeted Therapy: Advanced drugs target specific cancer cells without harming surrounding healthy tissue.
- Stage-Based Approach: Early stages may only need surgery, while later stages require a combination of treatments for effective results.
Prognosis and Prevention
Uterine Cancer Prognosis:
If diagnosed early, the five-year survival rate is about 80–90%. The chances decline in advanced stages.
Cervical Cancer Prognosis:
Early detection has a cure rate of over 90%, but late-stage diagnosis can be challenging to treat effectively.
Preventive Tips:
- For Uterine Cancer: Maintain a healthy weight, control diabetes, and manage hormones wisely.
- For Cervical Cancer: Get vaccinated for HPV and go for routine Pap smears and HPV tests.
Consult Cross Border Care Today
If you’re searching for expert care in gynecologic cancers, look no further than Cross Border Care, the best medical consultants in India. We will connect you to top cancer treatment hospitals in India. If you want affordable cancer treatment in India, contact us now!!
May 13, 2025