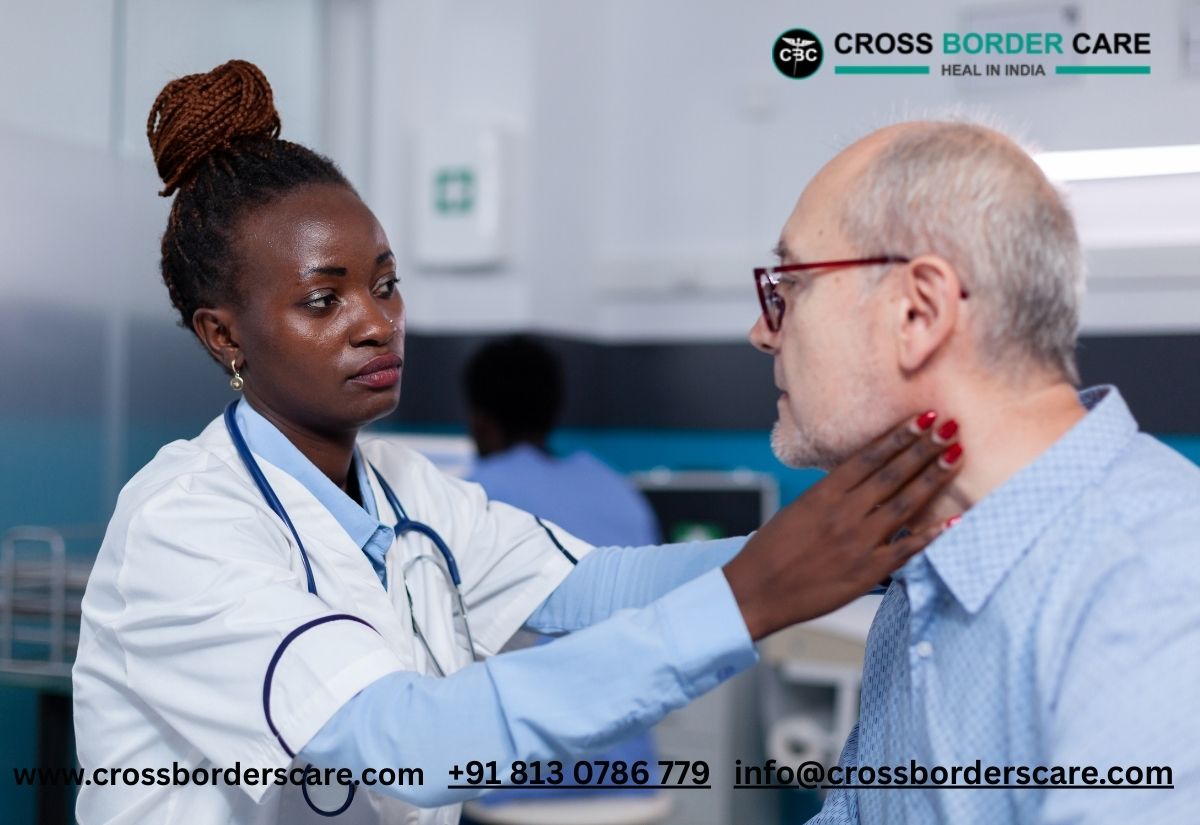
Knee Replacement Surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a medical procedure that helps to reduce chronic knee pain. It also helps restore knee joint function in patients whose knee joints have been severely damaged by injury or conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. This surgery involves the replacement of the damaged knee joint with artificial parts that are carefully made to replicate the natural structure and movement of the knee. Over the years, knee replacement surgery has become a very effective solution for increasing knee mobility, reducing discomfort, and improving patients’ overall quality of life suffering from complex knee conditions.
Procedure of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery usually takes a few hours to complete. The procedure of knee replacement surgery involves the following steps:
- Preoperative Evaluation: the surgeon thoroughly examines the patient’s knee and medical history before the surgery. This Evaluation helps determine the best surgical method.
- Anesthesia: On the day of surgery, the patient is either given general anesthesia to put them to sleep throughout the procedure or regional anesthesia, which numbs the lower part of the body.
- Incision: Once the anesthesia takes effect, the surgeon makes an incision on the knee joint to access the damaged area. In minimally invasive surgeries, smaller incisions are made to reduce tissue trauma and promote faster recovery.
- Reshaping of Bones: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon carefully removes the damaged cartilage and bone from the ends of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone).
- Implant Placement: The artificial components are attached to the prepared bone surfaces. These implants come in various shapes and sizes and are usually made of metal, plastic, or ceramic.
- Patellar Resurfacing: In some cases, the undersurface of the kneecap may also be resurfaced with a plastic component to improve movement and reduce friction with the new knee joint.
- Joint Stability and Range of Motion: Once the implants are in place, the surgeon checks the knee’s stability and range of motion and ensures that it moves smoothly and functions properly.
- Wound Closure: After placing the implants, the surgeon closes the incision with stitches or staples and applies dressings to protect the wound.
- Postoperative Recovery: The patient is taken to the recovery room for monitoring. Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a crucial role in the process of recovery. It helps the patient regain strength, flexibility, and mobility in the knee.
Types of TKR
There are different types of knee replacement surgeries that are performed according to the specific needs of patients. Each type of knee replacement surgery has its advantages and considerations, and the choice of procedure depends on various factors. It is important to consult an orthopedic surgeon to determine the best option. The main types of knee replacement surgery are:
- Total Knee Replacement: This is the most common type of knee replacement surgery. It involves the replacement of the entire knee joint with artificial components. TKR is recommended for patients with widespread knee arthritis or major joint damage.
- Partial Knee Replacement: PKR is performed when only one part of the knee joint is affected by arthritis or damage. It is also known as unicompartmental knee replacement. In this procedure, only the damaged area of the knee is replaced with an implant, thus preserving the healthy parts of the knee.
- Bilateral Knee Replacement: This surgery involves the replacement of both knee joints. It is usually performed on both knees during the same operation or as two different surgeries with a time gap in between.
- Revision Knee Replacement: In cases where a previous knee replacement has failed or worn out over time, revision knee replacement is performed to remove the old implants and replace them with new ones. This complex surgery addresses implant loosening, infection, or component malfunction.
- Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement: In recent years, the advancements in surgical techniques have led to minimally invasive robotic techniques, where smaller incisions are made. It leads to less tissue disruption and quicker recovery times.
- Gender-Specific Knee Replacement: Some manufacturers offer implants that are specially designed for male or female anatomy.
Risks associated with Knee replacement surgery
Knee replacement surgery is considered a safe and effective procedure. But like any other surgery, it has certain risks and potential complications. Some of the risks associated with knee replacement surgery are:
- Infection: There is a risk of an infection at the surgical site or in the knee joint. Infections can be treated with antibiotics, but in some cases, additional surgeries are required to remove the infected implants.
- Blood Clots: The surgery may increase the risk of developing blood clots in the legs or lungs. Blood-thinning medications are often used to minimize this risk.
- Implant Loosening or Wear: the artificial knee joint may become loose or worn out over time. It may lead to pain and reduced functionality. This may lead to another surgery to replace the implants.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: During the surgery, nerves or blood vessels near the knee can be injured, which may result in numbness, weakness, or bleeding.
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may experience allergic reactions to the materials used in the artificial knee implants.
- Persistent Pain: While knee replacement surgery often relieves chronic knee pain, some patients may experience persistent discomfort or pain even after the procedure.
- Stiffness or Limited Range of Motion: patients may have difficulty achieving full range of motion in the replaced knee, which may limit their mobility.
- Fracture: There is a risk of fracturing the bone during surgery, especially when removing damaged bone.
- Blood Loss: Knee replacement surgery can result in significant blood loss in some cases.
- Anesthesia Complications: Though complications related to anesthesia are very rare, they can occur sometimes.
Knee replacement surgery has helped millions of people to get rid of their knee problems and live a normal life again. It is important for the surgeon to discuss the risks with the patients before deciding to undergo knee replacement surgery. While the chances of experiencing complications are low, being aware of the risks allows patients to take necessary precautions to improve their chances of a successful outcome. Choosing an experienced surgeon and properly following the preoperative and postoperative instructions is also important.
August 3, 2023